Calculating and plotting degassing paths
Calculate degassing paths
A degassing path is a series of volatile concentrations both in the liquid and fluid that a magma will follow during decompression. In the VESIcal.calculate_degassing_path() calculation, the saturation pressure is computed, and then the system is equilibrated along a trajectory of decreasing pressure values at discrete steps. The default number of steps to calculate is 50, but this can be defined by the user by setting the argument steps to any integer value. If so desired, this calculation can be performed for any initial pressure, but the default is the saturation pressure. If a pressure is specified that is above the saturation pressure, the calculation will simlpy proceed from the saturation pressure, since the magma cannot degas until it reaches saturation.
Completely open-system, completely closed-system or partially open-system degassing paths can be calculated by specifying what proportion of the fluid to fractionate. The fluid fractionation value can range between 0 (closed-system: no fluid is removed, all is retained at each pressure step) and 1 (open-system: all fluid is removed, none is retained at each pressure step). Closed and partially open-system runs allow the user to speficy the initial presence of exsolved fluid that is in equilirium with the melt at the starting pressure.
Method structure:
Only single-sample calculations:
def calculate_degassing_path(self, sample, temperature, pressure='saturation', fractionate_vapor=0.0, init_vapor=0.0, steps=50).result
Required inputs:
sample: The composition of a sample. A single sample may be passed as a dictionary of values, with compositions of oxides in wt%.
temperature: The temperature in degres C.
Optional inputs:
pressure: The perssure at which to begin the degassing calculations, in bars. Default value is ‘saturation’, which runs the calculation with the initial pressure at the saturation pressure. If a pressure greater than the saturation pressure is input, the calculation will start at saturation, since this is the first pressure at which any degassing will occur.
fractionate_vapor: Proportion of vapor removed at each pressure step. Default value is 0.0 (completely closed-system degassing). Specifies the type of calculation performed, either closed system (0.0) or open system (1.0) degassing. If any value between <1.0 is chosen, user can also specify the ‘init_vapor’ argument (see below). A value in between 0 and 1 will remove that proportion of vapor at each step. For example, for a value of 0.2, the calculation will remove 20% of the vapor and retain 80% of the vapor at each pressure step.
init_vapor: Default value is 0.0. Specifies the amount of vapor (in wt%) coexisting with the melt before degassing.
steps: Default value is 50. Specifies the number of steps in pressure space at which to calcualte dissolved volatiles.
Calculated outputs: The function returns a pandas DataFrame with columns as: ‘Pressure_bars’, ‘H2O_liq’ and ‘CO2_liq’ (the concentration of H2O and CO2 in the liquid, in wt%), ‘XH2O_fl’ and ‘XCO2_fl’ (the composition of the H2O-CO2 fluid, in mol fraction), and ‘FluidProportion_wt’ (the proportion of fluid in the fluid-melt system, in wt%).
Import a data file and extract a single sample
myfile = v.BatchFile('../manuscript/example_data.xlsx')
SampleName = 'BT-ex'
extracted_bulk_comp = myfile.get_sample_composition(SampleName, asSampleClass=True)
Open system degassing calculation
open_df = v.calculate_degassing_path(sample=extracted_bulk_comp, temperature=900.0, fractionate_vapor=1.0).result
Closed system degassing calculation
closed_df = v.calculate_degassing_path(sample=extracted_bulk_comp, temperature=900.0).result
Partially closed system degassing calculation
half_df = v.calculate_degassing_path(sample=extracted_bulk_comp, temperature=900.0, fractionate_vapor=0.5).result
Closed system with initial fluid
exsolved_df = v.calculate_degassing_path(sample=extracted_bulk_comp, temperature=900.0, init_vapor=2.0).result
Calculate from initial pressure below saturation
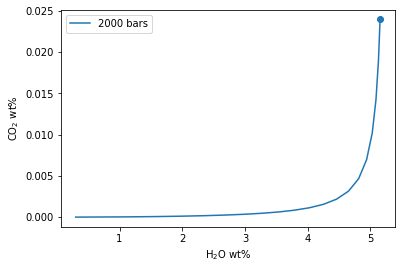
start2000_df = v.calculate_degassing_path(sample=extracted_bulk_comp, temperature=900.0, pressure=2000.0).result
Plotting degassing paths
Once degassing paths are calcualted, they may be easily plotted using VESIcal’s built in VESIcal.plot_degassing_paths() method. The user can plot multiple degassing paths on one plot. Optionally, labels in the plot legend can be specified.
Method structure:
plot(isobars=None, isopleths=None, degassing_paths=None, custom_H2O=None, custom_CO2=None,
isobar_labels=None, isopleth_labels=None, degassing_path_labels=None, custom_labels=None, **kwargs)
Required inputs to plot degassing paths:
degassing_paths: A list of DataFrames with degassing information as generated by calculate_degassing_path().
Optional inputs:
labels: Labels for the plot legend. Default is None, in which case each plotted line will be given the generic legend name of “Pathn”, with n referring to the nth degassing path passed. The user can pass their own labels as a list of strings.
Calculated outputs: The function returns a matplotlib object with the x-axis as H2O, wt% and the y-axis as CO2, wt%. All degassing paths passed are plotted on one figure.
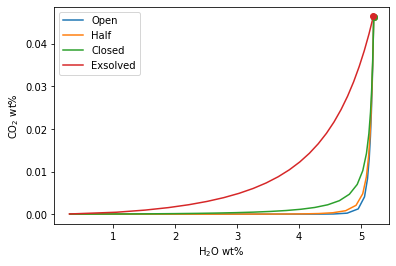
Plotting degassing paths from saturation pressure
fig, ax = v.plot(degassing_paths=[open_df, half_df, closed_df, exsolved_df],
degassing_path_labels=["Open", "Half", "Closed", "Exsolved"])
v.show()
Plotting degassing paths from 2000 bars
fig, ax = v.plot(degassing_paths=[start2000_df], degassing_path_labels=["2000 bars"])
v.show()